Publications
FIRST-AUTHOR PUBLICATIONS
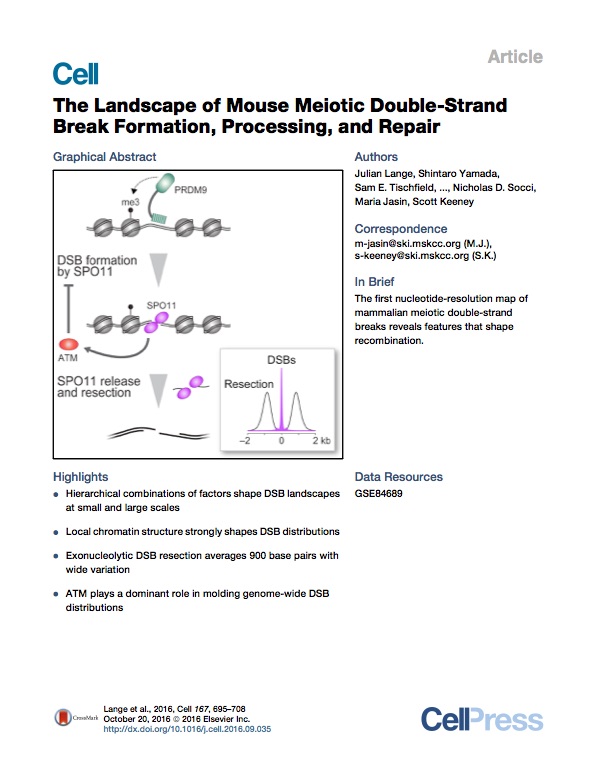
Lange et al. Cell 2016
Lange et al. Genomics 2013
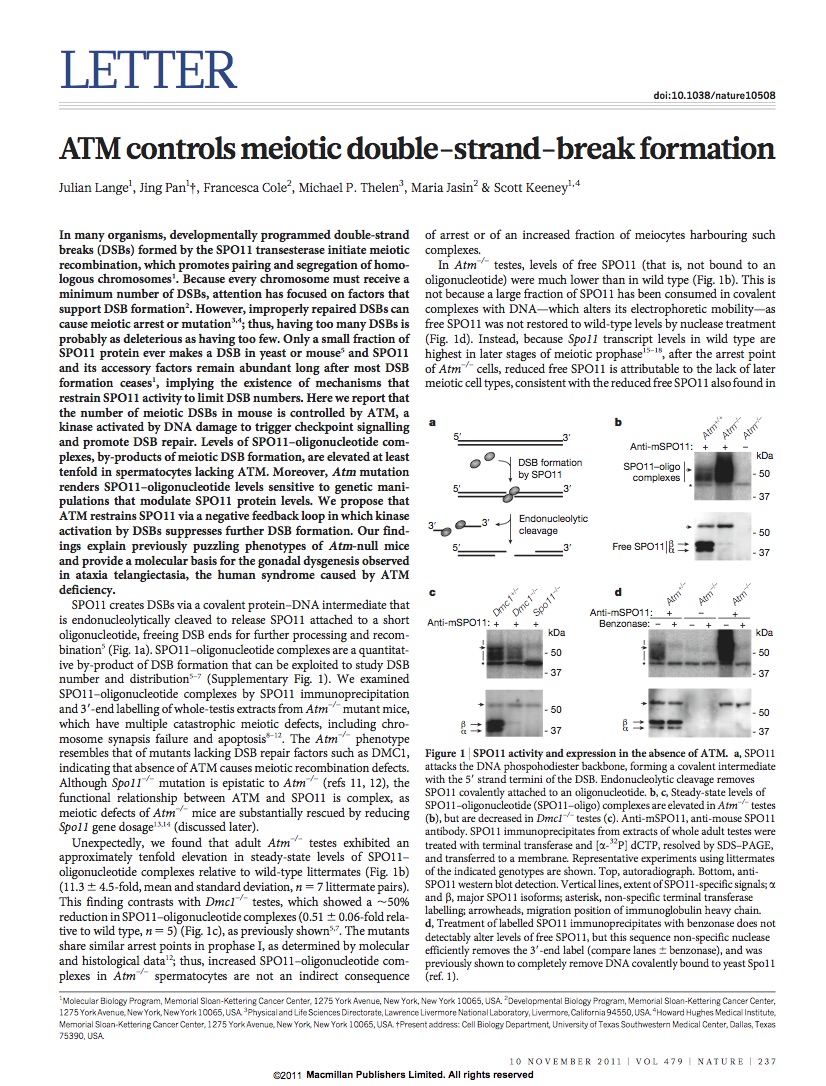
Lange et al. Nature 2011
Sasaki*, Lange* et al. NRMCB 2010
Lange et al. Cell 2009
Lange et al. NAR 2008 and website
Shattering the Genome
Lukaszewicz, Lange et al. De novo deletions and duplications at recombination hotspots in mouse germlines. Cell 2021
Dereli et al. Four-pronged negative feedback of DSB machinery in meiotic DNA-break control in mice. Nucleic Acids Research 2021
Lukaszewicz, Lange et al. Control of meiotic double-strand-break formation by ATM: local and global views. Cell Cycle 2018
Pacheco et al. ATR is required to complete meiotic recombination in mice. Nature Communications 2018
Widger et al. ATR is a multifunctional regulator of male mouse meiosis. Nature Communications 2018
Yamada et al. Genomic and chromatin features shaping meiotic double-strand break formation and repair in mice. Cell Cycle 2017
Jain et al. rahu is a mutant allele of Dnmt3c, encoding a DNA methyltransferase homolog required for meiosis and transposon repression in the mouse male germline. PLoS Genetics 2017
Stanzione et al. Meiotic DNA break formation requires the unsynapsed chromosome axis-binding protein IHO1 (CCDC36) in mice. Nature Cell Biology 2016
Lange et al. The landscape of mouse meiotic double-strand break formation, processing and repair. Cell 2016
Pacheco et al. The ATM signaling cascade promotes recombination-dependent pachytene arrest in mouse spermatocytes. PLoS Genetics 2015
Keeney, Lange, Mohibullah. Self-organization of meiotic recombination initiation: general principles and molecular pathways. Annual Review of Genetics 2014
Roset et al. The Rad50 hook domain regulates DNA damage signaling and tumorigenesis. Genes & Development 2014
Biswas et al. Meiotic cohesin SMC1β provides prophase I centromeric cohesion and is required for multiple synapsis-associated functions. PLoS Genetics 2013
Kauppi et al. Numerical constraints and feedback control of double-strand breaks in mouse meiosis. Genes & Development 2013
Cole et al. Homeostatic control of recombination is implemented progressively in mouse meiosis. Nature Cell Biology 2012
Lange et al. ATM controls meiotic double-strand-break formation. Nature 2011
Daniel, Lange et al. Meiotic homologue alignment and its quality surveillance are controlled by mouse HORMAD1. Nature Cell Biology 2011
Sasaki*, Lange*, Keeney. Genome destabilization by homologous recombination in the germ line. Nature Reviews Molecular Cellular Biology 2010 (*co-first author)
The Y Chromosome
San Roman et al. The human Y and inactive X chromosomes similarly modulate autosomal gene expression. Cell Genomics 2024
Lange* et al. Intrachromosomal homologous recombination between inverted amplicons on opposing Y-chromosome arms. Genomics 2013 (*co-corresponding author)
Lange et al. Isodicentric Y chromosomes and sex disorders as byproducts of homologous recombination that maintains palindromes. Cell 2009 [see news coverage in The New York Times]
Lange et al. MSY Breakpoint Mapper, a database of sequence-tagged sites useful in defining naturally occurring deletions in the human Y chromosome. Nucleic Acids Research 2008 [see user interface of database]
Repping et al. High mutation rates have driven extensive structural polymorphism among human Y chromosomes. Nature Genetics 2006
Repping et al. Recombination between palindromes P5 and P1 on the human Y chromosome causes massive deletions and spermatogenic failure. American Journal of Human Genetics 2002
Pediatric Cancer
Delattre et al. Un nouveau suppresseur de tumeur impliqué dans le modelage de la structure chromatinienne. Médecine Sciences 1998
Versteege et al. Truncating mutations of hSNF5/INI1 in aggressive paediatric cancers. Nature 1998